Answer:
[ I₂] = 0.015 M
[I] = 0.0044 M
Step-by-step explanation:
Let's consider the following reaction.
I₂(g) ⇄ 2 I(g)
The initial concentration of I₂ is:
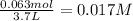
To find the concentrations at equilibrium we use an ICE Chart. We identify 3 stages (Initial, Change and Equilibrium) and complete each row with the concentration or change in concentration.
I₂(g) ⇄ 2 I(g)
I 0.017 0
C -x +2x
E 0.017-x 2x
The equilibrium constant (Kc) is:
![Kc=1.35 * 10^(-3) =([I]^(2) )/([I_(2)]) =((2x)^(2) )/((0.017-x)) \\4x^(2) +1.35 * 10^(-3)x - 2.3 * 10^(-5)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/964vxccgjauz9z3noc3r4djc2343822i2d.png)
x₁ = 0.0022 and x₂ = -0.0025. We take the positive value because it is the one with physical meaning.
[ I₂] = 0.017-x = 0.017-0.0022 = 0.015 M
[I] = 2x = 2(0.0022) = 0.0044 M