Answer: The standard Gibbs free energy change of the reaction is -32.9 kJ
Step-by-step explanation:
For the given chemical equation:
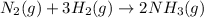
- The equation for the enthalpy change of the above reaction is:
![\Delta H^o_(rxn)=[(2* \Delta H^o_f_((NH_3(g))))]-[(1* \Delta H^o_f_((N_2(g))))+(3* \Delta H^o_f_((H_2(g))))]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/ak1bj22hjkcb81gu6jsousvu6cpxqdbf6x.png)
We are given:
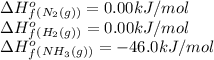
Putting values in above equation, we get:
![\Delta H^o_(rxn)=[(2* (-46.0))]-[(1* 0)+(3* 0)]=-92kJ=-92000J](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/fmlqwc6anno6lgl9luqipbk7ftc25hbn77.png)
- The equation for the entropy change of the above reaction is:
![\Delta S^o_(rxn)=[(2* \Delta S^o_((NH_3(g))))]-[(1* \Delta S^o_((N_2(g))))+(3* \Delta S^o_((H_2(g))))]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/89rpi44zkjjkq8d837csqq3c33c3rzbw8o.png)
We are given:
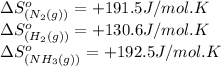
Putting values in above equation, we get:
![\Delta S^o_(rxn)=[(2* (192.5))]-[(1* (191.5))+(3* (130.6))]=-198.3J/K](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/m0x4vf61ecbsmzm6zpiatsn7onz4u9cgus.png)
- To calculate the standard Gibbs free energy of the reaction, we use the equation:
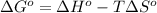
where,
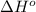 = standard enthalpy change = -92000 J
= standard enthalpy change = -92000 J
T = Temperature =
![25^oC=[273+25]K=298K](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/6roip9my7lmduj9zgvg2iw8f5svzc0eagc.png)
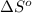 = standard entropy of the reaction = -198 J/K
= standard entropy of the reaction = -198 J/K
Putting values in above equation, we get:
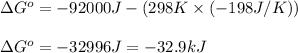
Hence, the standard Gibbs free energy change of the reaction is -32.9 kJ