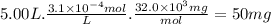Answer:
50 mg
Step-by-step explanation:
First, we have to calculate the partial pressure of O₂ (pO₂) using the following expression.
pO₂ = P × X(O₂) = 1.13 atm × 0.21 = 0.24 atm
where,
P: total pressure
X(O₂): mole fraction of oxygen
Then, we can calculate the concentration of O₂ in water (C) using Henry's law.
C = k × pO₂ = (1.3 × 10⁻³ M/atm) × 0.24 atm = 3.1 × 10⁻⁴ M
where,
k: Henry's constant for O₂
The mass of oxygen in a 5.00 L bucket with a concentration of 3.1 × 10⁻⁴ M is: (MM 32.0 g/mol)