Answer:
The correct answer is 0.024 M
Step-by-step explanation:
First we use an ICE table:
Br₂(g) + F₂(g) ⇔ 2 BrF(g)
I 0.111 M 0.111 M 0
C -x -x 2 x
E 0.111 -x 0.111-x 2x
Then, we replace the concentrations of reactants and products in the Kc expression as follows:
Kc=
![([BrF ]^(2) )/([ F_(2) ][Br_(2) ])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/vq6f0bwe4orjhe9hi6hfi4h9cfxp0zq75n.png)
Kc=
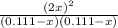
54.7=
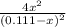
We can take the square root of each side of the equation and we obtain:
7.395=
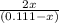
0.111(7.395) - 7.395x= 2x
0.82 - 7.395x= 2x
0.82= 2x + 7.395x
⇒ x= 0.087
From the x value we can obtain the concentrations in the equilibrium:
[F₂]= [Br₂]= 0.111 -x= 0.111 - 0.087= 0.024 M
[BrF]= 2x= 2 x (0.087)= 0.174 M
So, the concentration of fluorine (F₂) at equilibrium is 0.024 M.