Answer:
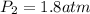
Step-by-step explanation:
The question molded an ideal gas law, which state in part
"The Volume(V) of a gas is directly proportional to the absolute temperature(T) and inversely proportional to the pressure(P)"
Mathematically, this can be expressed as
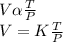
where K is a constant. varying the value of k, we arrive at
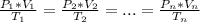
using the first two expression of the above equation, where
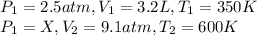
Note, we have to convert the volume to
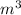
since

Now
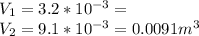
also we convert the pressure from atm to pascal(pa)
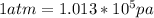

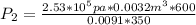
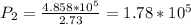
convert back to atm
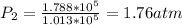
Hence the value of he final pressure is
1.8atm