Answer:
Molar mass = 180 g/mol
Ka = 3.31x10⁻⁴
Step-by-step explanation:
Because the acetylsalicylic is a monoprotic acid, it only leaves 1 mol of H⁺ in the reaction, so, it's necessary 1 mol of NaOH for each 1 mol of acetylsalicylic acid. The number of moles of NaOH is the volume, in L, multiplied by the concentration:
n = 0.03015*0.5137 = 0.01549
Which is also the number of moles of the acid. The molar mass is the mass, in g, divided by the number of moles:
M = 2.79/0.01549
M = 180 g/mol
After reacting with the base, the conjugate base of the acid will be formed, and the equilibrium between the acid form (HA) and the conjugate base (A⁻) is a buffer. It formed 0.01549 moles of A⁻, which will react with the moles of H⁺ from HCl to form HA.
nH⁺ = nHCl = 0.01741*0.448 = 0.0078 mol
A⁻ + H⁺ ⇄ HA
0.01549 0.0078 0 Initial
-0.0078 -0.0078 +0.0078 Reacts
0.0078 0 0.0078 Equilibrium
For a buffer, the pH can be calculated by the Handerson-Halsebach equation:
pH = pKa + log[A⁻]/[HA]
Because the volume is the same, we can use the number of moles instead of the concentration:
3.48 = pKa + log(0.0078/0.0078)
pKa = 3.48
pKa = -logKa
Ka =
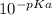
Ka =
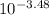
Ka = 3.31x10⁻⁴