Step-by-step explanation:
Any change in the equilibrium is studied on the basis of Le-Chatelier's principle.
This principle states that if there is any change in the variables of the reaction, the equilibrium will shift in the direction to minimize the effect.
Increase the volume
If the volume of the container is increased, the pressure will decrease according to Boyle's Law.
Now, according to the Le-Chatlier's principle, the equilibrium will shift in the direction where increase in pressure is taking place.And in order balance pressure reaction will go in direction where gaseous moles are more.
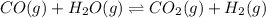 (volume is decreased)
(volume is decreased)
Number of moles of gases are same on both sides so, equilibrium will not get effected by increasing the volume.
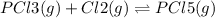 (volume is increased)
(volume is increased)
On increasing volume pressure increases the gaseous moles on reactant sides are more so, the reaction will shift in left direction.
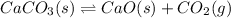 (volume is increased)
(volume is increased)
On increasing volume pressure increases the gaseous moles on product sides are more so, the reaction will shift in right direction.