Answer:
2.42 x 10^5 Pa
Step-by-step explanation:
Volume flow, V = 7000 cm^3/s
Radius, r1 = 3.8 cm
P1 = 2.5 x 10^5 Pa
r2 = 2.25 cm
Let v1 be the velocity of water at one end.
Volume flow per second = area x velocity
7000 = 3.14 x 3.8 x 3.8 x v1
v1 = 154.38 cm/s = 1.54 m/s
Use of equation of continuity
A1 x v1 = A2 x v2
π x r1² x v1 = π x r2² x v2
3.8 x 3.8 x 154.38 = 2.25 x 2.25 x v2
v2 = 440.35 cm/s = 4.40 m/s
By use of Bernoullie's theorem
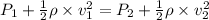
2.5 x 10^5 + 0.5 x 1000 x 1.54 x 1.54 = P2 + 0.5 x 1000 x 4.40 x 4.40
2.5 x 10^5 + 1185.8 = P2 + 9680
P2 = 2.42 x 10^5 Pa
Thus, the pressure at the other end is 2.42 x 10^5 Pa.