Answer:
0.014 M/s
Step-by-step explanation:
The rate of a chemical reaction is defined as the change in the concentration of the products or reactants over a specific period of time. The reaction rate can be calculated by dividing the change in concentration of the reactants products by the time elapsed for the given reaction. The reaction rate can also be calculated bu using:
![r = k*[CH_(3)Br]*[NaOH]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/7k0hjpvr8dvggfd68jk0d85jzoaenn3qsl.png)
where:
r is the rate of the reaction, k is the rate constant, and [] signifies the concentration of the compound.
When the concentrations of
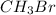 and NaOH are both 0.140 M, the rate of the reaction is 0.0070 M/s.
and NaOH are both 0.140 M, the rate of the reaction is 0.0070 M/s.
Therefore, when the concentration of
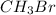 is doubled, the rate of the reaction will also be doubled, i.e. r = 2* 0.0070 = 0.014 M/s
is doubled, the rate of the reaction will also be doubled, i.e. r = 2* 0.0070 = 0.014 M/s