Answer:
-48
Explanation:
Lets call L(x,y) = 10y²x, M(x,y) = 4x²y. Green's Theorem stays that the line integral over C can be calculed by computing the double integral over the inner square of Mx - Ly. In other words
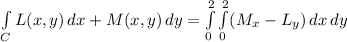
Where Mx and Ly are the partial derivates of M and L with respect to the x variable and the y variable respectively. In other words, Mx is obtained from M by derivating over the variable x treating y as constant, and Ly is obtaining derivating L over y by treateing x as constant. Hence,
- M(x,y) = 4x²y
- Mx(x,y) = 8xy
- L(x,y) = 10y²x
- Ly(x,y) = 20xy
- Mx - Ly = -12xy
Therefore, the line integral can be computed as follows
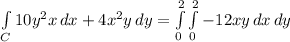
Using the linearity of the integral and Barrow's Theorem we have
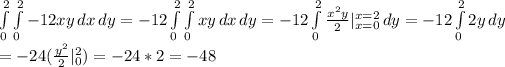
As a result, the value of the double integral is -48-