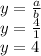Answer:
Vertical asymptote:

Horizontal asymptote:
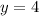
Explanation:
Given:
The function is given as:
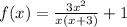
First, we will simplify the given function.
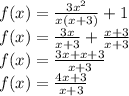
Now, vertical asymptotes occur when denominator is 0. So,
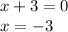
Therefore, the vertical asymptote is:

When the degree of numerator is equal to that of the denominator, we have horizontal asymptote equal to
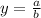 where, 'a' is the leading coefficient of numerator and 'b' is the leading coefficient of denominator.
where, 'a' is the leading coefficient of numerator and 'b' is the leading coefficient of denominator.
Here, degree of numerator and denominator are same and equal to 1. The value of 'a' is 4 and 'b' is 1. So, horizontal asymptote is given as: