Answer:
![(mg)/(L)[Carbonate]=0.33X50=16.5(mg)/(L) CaCO_(3)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/7y4znxiryw2xlekyxgm6xkzz18e0yvhx42.png)
![(mg)/(L)[BiCarbonate]=1.06X50=53(mg)/(L) CaCO_(3)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/74o0jibx3ie9yl2j5bgmt5blukx29dz410.png)
Step-by-step explanation:
The milli equivalents of the carbonate and bicarbonate ions can be calculated by multiplying the milligrams of the two with their respective equivalent mass.
The equivalent mass of
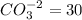
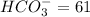
milliequivalents of carbonate will be:
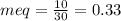
millieuivalents of bicarbonate will be:
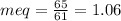
In terms of calcium carbonate, we will multiply the milliequivalents with 50 (the equivalent weight of calcium carbonate).
![(mg)/(L)[Carbonate]=0.33X50=16.5(mg)/(L) CaCO_(3)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/7y4znxiryw2xlekyxgm6xkzz18e0yvhx42.png)
![(mg)/(L)[BiCarbonate]=1.06X50=53(mg)/(L) CaCO_(3)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/74o0jibx3ie9yl2j5bgmt5blukx29dz410.png)