Step-by-step explanation:
It is known that relation between entropy, heat energy and temperature is as follows.
dS =
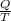
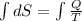
Also we know that at constant pressure, Q =
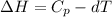
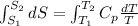
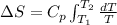
As the given data is as follows.
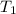 = 298 K,
= 298 K,
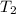 = 348 K
= 348 K
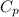 = 29.355 J/K mol
= 29.355 J/K mol
Now, putting the given values into the above formula as follows.
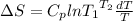
=
![29.355 [ln (348) - ln (298)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/yuhm7hq16qbpbnqna5atcmmrh6yq81oull.png)
=
![29.355 [5.85 - 5.69]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/12ucrdxo2j8a296c9ldcua4raxtpheu5fr.png)
= 4.48 J/k mol
Thus, we can conclude that the increase in the molar entropy of given oxygen gas is 4.48 J/k mol.