Answer:
6.29 J/(g*K)
Step-by-step explanation:
Hi, you haven't provided the equation that we need for the calculation of entropy change. However, the equation below will be used for the calculation:
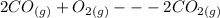
Δ
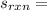 2*Δ
2*Δ
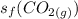 ] - [2*Δ
] - [2*Δ
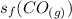 + Δ
+ Δ
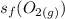 ]
]
Δ
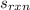 is the standard entropy change for the reaction [J/(mol.K)]
is the standard entropy change for the reaction [J/(mol.K)]
Δ
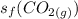 is the standard entropy of formation of carbon dioxide gas = 213.79 J/(mol.K)
is the standard entropy of formation of carbon dioxide gas = 213.79 J/(mol.K)
Δ
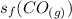 is the standard entropy of formation of carbon monoxide gas = 197.66 J/(mol.K)
is the standard entropy of formation of carbon monoxide gas = 197.66 J/(mol.K)
Δ
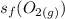 is the standard entropy of formation of oxygen gas = 205.03 J/(mol.K)
is the standard entropy of formation of oxygen gas = 205.03 J/(mol.K)
Therefore,
Δ
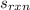 = [2*213.79] - [2*197.66+205.03] = - 172.77 J/(mol*K)
= [2*213.79] - [2*197.66+205.03] = - 172.77 J/(mol*K)
From the given chemical reaction, when 2 moles of carbon monoxide gas reacts, the entropy change for the reaction -172.77 J/(mol*K). Therefore, when 2.04 moles of carbon monoxide gas reacts, the entropy change for the reaction is -172.77*2.04/2 = -176.23 J/(mol*K).
Thus, converting J/(mol*K) to J/(g*K):
molar mass of carbon monoxide is 28 g/mol.
Thus, the entropy change in J/(g*K) = -176.23/28 = 6.29 J/(g*K)