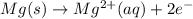Answer : The half-cell reaction occurs at the anode is,
(B)
Explanation :
Galvanic cell : It is defined as a device which is used for the conversion of the chemical energy produces in a redox reaction into the electrical energy. It is also known as the voltaic cell or electrochemical cell.
In the galvanic cell, the oxidation occurs at an anode which is a negative electrode and the reduction occurs at the cathode which is a positive electrode.
Redox reaction or Oxidation-reduction reaction : It is defined as the reaction in which the oxidation and reduction reaction takes place simultaneously.
Oxidation reaction : It is defined as the reaction in which a substance looses its electrons. In this, oxidation state of an element increases. Or we can say that in oxidation, the loss of electrons takes place.
Reduction reaction : It is defined as the reaction in which a substance gains electrons. In this, oxidation state of an element decreases. Or we can say that in reduction, the gain of electrons takes place.
The given two-half reactions are:
(1)
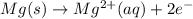
(2)
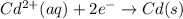
According to the galvanic cell, the half-cell reaction (1) shows oxidation reaction so, it occurs at anode and the half-cell reaction (2) shows reduction reaction so, it occurs at cathode.
Hence, the half-cell reaction occurs at the anode is,