Answer:
The response factor for X relative to S is 0,105
Concentration of X in the unknown solution is: 18,3mM
Step-by-step explanation:
The response factor of X is:
RF x = peak area / concentration = 925
And of S:
RF s = 10829 / 1,23 = 8804
The response factor for X relative to S is:
RRF = 925/8804 = 0,105
Concentration of S in the unknown solution is:
8,27mM×
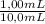 = 0,827mM
= 0,827mM
-Because the 1,00 mL of S was diluted from 1,00mL to 10,0mL-
Using the RRF formula:
Conc X = Peak area X* Concentration B / peak area S * RRF
[X] = 5389*0,827mM / 4627*0,105
[X] = 9,17mM in the 10,0mL solution.
In the unknown solution:
9,17mM×
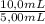 = 18,3mM
= 18,3mM
I hope it helps!