Answer: Order with respect to A is 1 , order with respect to B is 0 and total order is 1
Step-by-step explanation:
Rate law says that rate of a reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of the reactants each raised to a stoichiometric coefficient determined experimentally called as order.
![Rate=k[A]^x[B]^y](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/wq5ji9hbq4g6rx67qjbipwqn72erwdi258.png)
k= rate constant
x = order with respect to A
y = order with respect to A
n = x+y = Total order
a) From trial 1:
![3.20* 10^(-1)=k[1.50]^x[1.50]^y](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/ujcmzl0hd6jfh4s1jl6p50v4k06w2gdtkp.png) (1)
(1)
From trial 2:
![3.20* 10^(-1)=k[1.50]^x[2.50]^y](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/qirqy8gr0bjz706bstvp81wnnifchr65pa.png) (2)
(2)
Dividing 2 by 1 :
![(3.20* 10^(-1))/(3.20* 10^(-1))=(k[1.50]^x[2.50]^y)/(k[1.50]^x[1.50]^y)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/4770mue2qshwqdt5k3k96j64ppn82bk9bg.png)
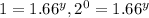 therefore y=0
therefore y=0
b) From trial 2:
![3.20* 10^(-1)=k[1.50]^x[2.50]^y](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/qirqy8gr0bjz706bstvp81wnnifchr65pa.png) (3)
(3)
From trial 3:
![6.40* 10^(-1)=k[3.00]^x[1.50]^y](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/jelo94pys2lzzgllqwk7ntzbrbgsbf84v3.png) (4)
(4)
Dividing 4 by 3:
![(6.40* 10^(-1))/(3.20* 10^(-1))=(k[3.00]^x[1.50]^y)/(k[1.50]^x[2.50]^y)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/e9o92pttf126j0kxo78mwd6zrk8xyqooie.png)
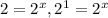 , x=1
, x=1
Thus rate law is
![Rate=k[A]^1[B]^0](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/q3z7af0b94mqs0s4hoc9rcn5eac11573ft.png)
Thus order with respect to A is 1 , order with respect to B is 0 and total order is 1+0=1.