The concept required to solve this problem is that of the Doppler effect which is defined as the change in frequency of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the wave source
Mathematically it can be expressed as
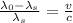
Where,
c = Speed of light
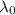 = Peak wavelength
= Peak wavelength
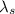 = Peak Wavelength observed
= Peak Wavelength observed
Our values are given as,
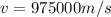
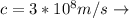 Speed of light
Speed of light
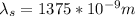
Basically what we should look for is that 'relative' frequency that is emitted when the star moves away so we clear
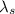
Replacing we have,
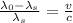
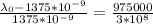
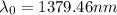
Therefore the peak wavelength that is observed when the star is traveling away from the eart to the velocity given is 1379.46nm