Answer: -1111.6 kJ
Step-by-step explanation:
According to Hess’s law of constant heat summation, the heat absorbed or evolved in a given chemical equation is the same whether the process occurs in one step or several steps.
According to this law, the chemical equation can be treated as ordinary algebraic expression and can be added or subtracted to yield the required equation. That means the enthalpy change of the overall reaction is the sum of the enthalpy changes of the intermediate reactions.
The given chemical reaction is,
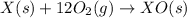
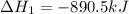 (1)
(1)
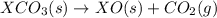
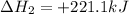 (2)
(2)
Now we have to determine the value of
 for the following reaction i.e,
for the following reaction i.e,
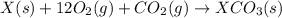
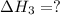 (3)
(3)
Subtracting (1) and (2) we get (3)
So, the value
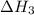 for the reaction will be:
for the reaction will be:
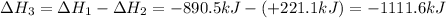
Hence, the value of
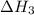 for the reaction is -1111.6 kJ
for the reaction is -1111.6 kJ