Answer:
-4.7°C
Step-by-step explanation:
The freezing point depression is a colligative property that can be calculated using the following expression.
ΔTf = Kf . b
where
ΔTf: depression in the freezing point
Kf: molal freezing point depression constant
b: molality
The moles of urea (solute) are:
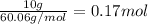
The mass of solvent (X) is 500 g (0.500 kg).
The molality of the urea is:
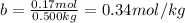
ΔTf = Kf . b = (6.19 °C.kg/mol) × 0.34 mol/kg = 2.1°C
The freezing point of pure X is:
-6.8°C + 2.1°C = -4.7°C