Answer : The correct options are:
(a) H₂S/HS⁻
(b) H₃PO₄/KH₂PO₄
(d) CH₃CO₂H/NaCH₃CO₂
Explanation :
According to the Bronsted Lowry concept, Bronsted Lowry-acid is a substance that donates one or more hydrogen ion in a reaction and Bronsted Lowry-base is a substance that accepts one or more hydrogen ion in a reaction.
Or we can say that, conjugate acid is proton donor and conjugate base is proton acceptor.
The general equilibrium reaction will be,
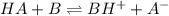
In this reaction,
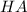 is an acid that donate a proton or hydrogen to
is an acid that donate a proton or hydrogen to
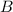 base and it forms
base and it forms
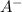 and
and
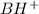 are conjugate base and acid respectively.
are conjugate base and acid respectively.
That means,
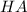 and
and
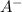 are conjugate acid base pair and
are conjugate acid base pair and
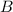 and
and
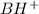 are conjugate base acid pair.
are conjugate base acid pair.
(a) H₂S/HS⁻
This pair of compound represent a conjugate acid base pair.
(b) H₃PO₄/KH₂PO₄
This pair of compound represent a conjugate acid base pair.
(c) Ca(OH)₂/CaSO₄
This pair of compound does not represent a conjugate acid base pair because Ca(OH)₂ is strong base, it can accept a proton from conjugate acid.
(d) CH₃CO₂H/NaCH₃CO₂
This pair of compound represent a conjugate acid base pair.