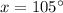Answer:
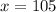 °
°
Explanation:
Given:
Let us label the vertices of the figure as shown below.
Consider triangle CDE. The exterior angle CDB is equal to the sum of opposite interior angles. Therefore,
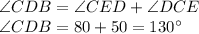
Now, for a quadrilateral ABDX, the exterior angle DXC is given as:
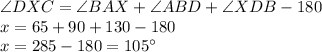
Therefore,