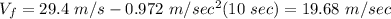Answer:
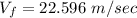
Step-by-step explanation:
Physics Dynamics
The second Newton's Law, states the acceleration of a body will depend on the net force applied to it and its mass. If an object is left on free air the net force acting on it is the gravitational force. It will continue to fall with accelerated motion until that force is changed.
The formulas needed to compute the physics dynamics magnitudes are
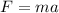
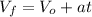
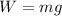
The variables involved are: F=net force, m=mass, a=acceleration,
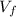 = final velocity,
= final velocity,
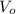 = initial velocity, t = time, W = Weigh, g=
= initial velocity, t = time, W = Weigh, g=
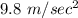
At first, only the gravitational force of 605 N acts on the parachutist. That net force is due to the parachutist's weigh. We can know the mass
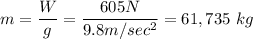
If we assume the initial speed is 0, then
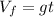
All variables are assumed to be positive downwards. So, when t=3 sec
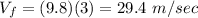
Right then an air resistance force of 665 N appears. The new net force is
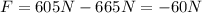
The new acceleration will be
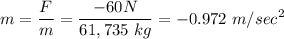
The acceleration is now negative since it goes upward. We are required to compute the speed after 10 sec (not clear if it's after this last event or it comes from the initial condition). We assume those 10 sec come from the very beginning of the jump, so t=7 sec
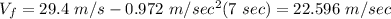
If it was t= 10\ sec