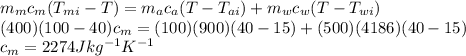Answer:
2274 J/kg ∙ K
Step-by-step explanation:
The complete statement of the question is :
A lab assistant drops a 400.0-g piece of metal at 100.0°C into a 100.0-g aluminum cup containing 500.0 g of water at 15 °C. In a few minutes, she measures the final temperature of the system to be 40.0°C. What is the specific heat of the 400.0-g piece of metal, assuming that no significant heat is exchanged with the surroundings? The specific heat of this aluminum is 900.0 J/kg ∙ K and that of water is 4186 J/kg ∙ K.
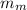 = mass of metal = 400 g
= mass of metal = 400 g
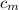 = specific heat of metal = ?
= specific heat of metal = ?
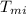 = initial temperature of metal = 100 °C
= initial temperature of metal = 100 °C
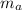 = mass of aluminum cup = 100 g
= mass of aluminum cup = 100 g
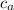 = specific heat of aluminum cup = 900.0 J/kg ∙ K
= specific heat of aluminum cup = 900.0 J/kg ∙ K
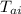 = initial temperature of aluminum cup = 15 °C
= initial temperature of aluminum cup = 15 °C
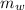 = mass of water = 500 g
= mass of water = 500 g
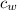 = specific heat of water = 4186 J/kg ∙ K
= specific heat of water = 4186 J/kg ∙ K
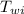 = initial temperature of water = 15 °C
= initial temperature of water = 15 °C
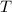 = Final equilibrium temperature = 40 °C
= Final equilibrium temperature = 40 °C
Using conservation of energy
heat lost by metal = heat gained by aluminum cup + heat gained by water