Answer:
t = 5.59x10⁴ y
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the time for the ¹⁴C drops to 1.02 decays/h, we need to use the next equation:
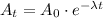 (1)
(1)
where
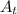 : is the number of decays with time, A₀: is the initial activity, λ: is the decay constant and t: is the time.
: is the number of decays with time, A₀: is the initial activity, λ: is the decay constant and t: is the time.
To find A₀ we can use the following equation:
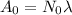 (2)
(2)
where N₀: is the initial number of particles of ¹⁴C in the 1.03g of the trees carbon
From equation (2), the N₀ of the ¹⁴C in the trees carbon can be calculated as follows:
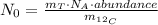
where
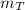 : is the tree's carbon mass,
: is the tree's carbon mass,
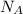 : is the Avogadro's number and
: is the Avogadro's number and
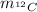 : is the ¹²C mass.
: is the ¹²C mass.
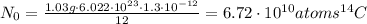
Similarly, from equation (2) λ is:
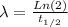
where t 1/2: is the half-life of ¹⁴C= 5700 years
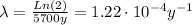
So, the initial activity A₀ is:
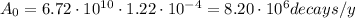
Finally, we can calculate the time from equation (1):

I hope it helps you!