Answer:
The firm is having a negative profit or loss of $51.75.
Step-by-step explanation:
The cost function of a perfectly competitive firm is given as C = 64 + 15q + q2.
The marginal cost is MC = 15 + 2q.
The market price of the product is given as $22.
Each firm is producing 3.5 units in the short run.
The profit or loss to the firm is the difference between total revenue earned and the total cost incurred.
Total cost
= 64 + 15q + q2
= 64 + 15
 3.5 +
3.5 +
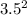
= 64 + 52.5 + 12.25
= 128.75
Total revenue
= Price
 Quantity
Quantity
= $22
 3.5
3.5
= $77
Profits
= Total revenue - Total cost
= $77 - $128.75
= - $51.75