Answer:
Final velocity, v = 0.28 m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that,
Mass of the model,
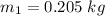
Speed of the model,
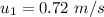
Mass of another model,
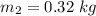
Initial speed of another model,
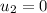
To find,
Final velocity
Solution,
Let V is the final velocity. As both being soft clay, they naturally stick together. It is a case of inelastic collision. Using the conservation of linear momentum to find it as :
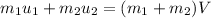
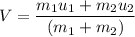
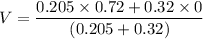
V = 0.28 m/s
So, their final velocity is 0.28 m/s. Hence, this is the required solution.