Answer:
For 1: The partial pressure of helium is 376 mmHg and that of methane gas is 445 mmHg
For 2: The mole fraction of nitrogen gas is 0.392 and that of carbon dioxide gas is 0.608
Step-by-step explanation:
For 1:
To calculate the number of moles, we use the equation:
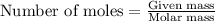 .....(1)
.....(1)
Given mass of helium = 0.723 g
Molar mass of helium = 4 g/mol
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
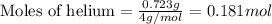
Given mass of methane gas = 3.43 g
Molar mass of methane gas = 16 g/mol
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
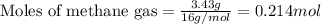
To calculate the mole fraction , we use the equation:
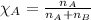 .......(2)
.......(2)
To calculate the partial pressure of gas, we use the equation given by Raoult's law, which is:
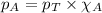 ......(3)
......(3)
We are given:
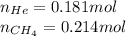
Putting values in equation 2, we get:
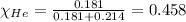
Calculating the partial pressure by using equation 3, we get:
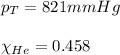
Putting values in equation 3, we get:
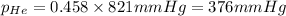
We are given:
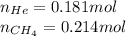
Putting values in equation 2, we get:
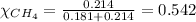
Calculating the partial pressure by using equation 3, we get:
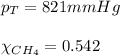
Putting values in equation 3, we get:

Hence, the partial pressure of helium is 376 mmHg and that of methane gas is 445 mmHg
We are given:
Partial pressure of nitrogen gas = 363 mmHg
Partial pressure of carbon dioxide gas = 564 mmHg
Total pressure = (363 + 564) mmHg = 927 mmHg
Calculating the mole fraction of the gases by using equation 3:
For nitrogen gas:
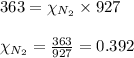
For carbon dioxide gas:
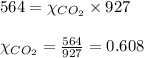
Hence, the mole fraction of nitrogen gas is 0.392 and that of carbon dioxide gas is 0.608