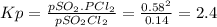Answer:
(a) pSO₂Cl₂ = 0.14 atm
pSO₂ = pCl₂ = x = 0.58 atm
(b) Kp = 2.4
Step-by-step explanation:
Let's consider the following reaction.
SO₂Cl₂(g) ⇄ SO₂(g) + Cl₂(g)
We can calculate the initial pressure of SO₂Cl₂ using the ideal gas equation.
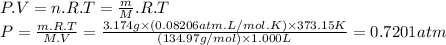
We can find the partial pressures at equilibrium using an ICE chart. In this chart, we complete each row with the pressure or change in pressure in each stage.
SO₂Cl₂(g) ⇄ SO₂(g) + Cl₂(g)
I 0.7201 0 0
C -x +x +x
E 0.7201 - x x x
At equilibrium, the sum of partial pressures is equal to the total pressure.
pSO₂Cl₂ + pSO₂ + pCl₂ = 1.30 atm
(0.7201 - x) + x + x = 1.30 atm
x = 0.58 atm
pSO₂Cl₂ = 0.7201 - x = 0.14 atm
pSO₂ = pCl₂ = x = 0.58 atm
The equilibrium constant (Kp) is: