Answer:
0.0495 M/s
Step-by-step explanation:
Rate of reaction (r) = Δ[
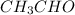 ]/Δt
]/Δt
Therefore, using the data given:
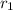 = (0.2480-0.1172)M/(1000-0)s =
= (0.2480-0.1172)M/(1000-0)s =
 M/s
M/s
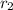 = (0.1172-0.0767)M/(2000-1000)s =
= (0.1172-0.0767)M/(2000-1000)s =
 M/s
M/s
Using the rate law:
![r = k*[CH_(3)CHO] ^(m)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/mwuwim1betytohjgm8uvb4m0la5ygf6ooi.png)
r is the rate of the reaction (M/s), k is the rate constant (M/s), and m is a number.
Therefore, we have:
![r_(1) = k*[0.1172]^(m)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/3bnoi5tcw5ahgh8qg892o49y7wnh5osbls.png) (1)
(1)
![r_(2) = k*[0.0767]^(m)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/ayfpyyqou7odsr0i1njxqcjhieoz2ze1i0.png) (2)
(2)
Divide equation (1) by equation 2, we have:
![(r_(1) )/(r_(2) ) = [(0.1172)/(0.0767)] ^(m)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/fwpsuziqx7krfyacd1y4hegsqsa0a419os.png)
using
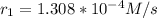 and
and

We have:
![(1.308*10^(-4) )/(4.05*10^(-5) ) = [(0.1172)/(0.0767) ]^(m)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/u6ocub23t20nj1fifrzpcscva32afrm44o.png)
Thus:
3.2296 =
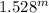
Taking log of both sides, we have
log (3.2296) = m*log (1.528), and m = 2.77 (approximately 3)
Therefore, using equation (1) to get the rate constant (k), we have:
![1.308*10^(-4) (M/s) = k*[0.1172]^(2.77)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/b9zywtuh44a4lncxh787sc4ttwhje1vtbj.png)
Thus k = 0.0001308/0.00264 = 0.0495 M/s
Thus, the rate constant is 0.0495 M/s