Answer: The mass of the substance that must be added is 75.2 grams.
Step-by-step explanation:
Elevation in boiling point is defined as the difference in the boiling point of solution and freezing point of pure solution.
The equation used to calculate elevation in boiling point follows:
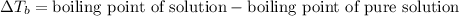
 = ? °C
= ? °C
Boiling point of pure water = 100°C
Boiling point of solution = 101.54°C
Putting values in above equation, we get:
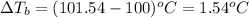
To calculate the elevation in boiling point, we use the equation:
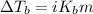
Or,
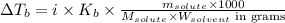
where,
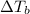 = 1.54°C
= 1.54°C
i = Vant hoff factor = 1 (For non-electrolytes)
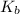 = molal boiling point elevation constant = 0.512°C/m.g
= molal boiling point elevation constant = 0.512°C/m.g
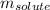 = Given mass of solute = ? g
= Given mass of solute = ? g
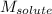 = Molar mass of solute = 50.0 g/mol
= Molar mass of solute = 50.0 g/mol
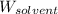 = Mass of solvent (water) = 500 g
= Mass of solvent (water) = 500 g
Putting values in above equation, we get:
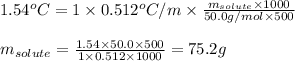
Hence, the mass of substance that must be added is 75.2 grams.