Answer: The enthalpy change of the reaction is -243 J/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
The heat released by the reaction is absorbed by the calorimeter and the solution.
The chemical equation used to calculate the heat released follows:
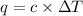
where,
c = heat capacity of calorimeter = 1620 J/K
 = change in temperature =
= change in temperature =
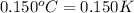 (Change remains same)
(Change remains same)
Putting values in above equation, we get:
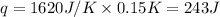
Sign convention of heat:
When heat is absorbed, the sign of heat is taken to be positive and when heat is released, the sign of heat is taken to be negative.
For the given chemical reaction:
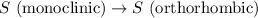
We are given:
Moles of monoclinic sulfur = 1 mole
- To calculate the enthalpy change of the reaction, we use the equation:
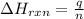
where,
q = amount of heat released = -243 J
n = number of moles = 1 mole
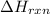 = enthalpy change of the reaction
= enthalpy change of the reaction
Putting values in above equation, we get:
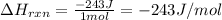
Hence, the enthalpy change of the reaction is -243 J/mol