Answer:
Moles of potassium chlorate reacted = 0.2529 moles
The amount of oxygen gas collected will be 12.8675 g
Step-by-step explanation:
(a)
We are given:
Vapor pressure of water = 17.5 mmHg
Total vapor pressure = 748 mmHg
Vapor pressure of Oxygen gas = Total vapor pressure - Vapor pressure of water = (748 - 17.5) mmHg = 730.5 mmHg
To calculate the amount of Oxygen gas collected, we use the equation given by ideal gas which follows:
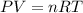
where,
P = pressure of the gas = 730.5 mmHg
V = Volume of the gas = 9.49 L
T = Temperature of the gas =
![20^oC=[20+273]K=293K](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/2rqkt68ddzsgrhhdiygdxv8hg4exf1j7bf.png)
R = Gas constant =
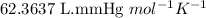
n = number of moles of oxygen gas = ?
Putting values in above equation, we get:
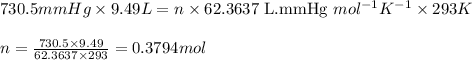
According to the reaction shown below as:-
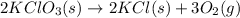
3 moles of oxygen gas are produced when 2 moles of potassium chlorate undergoes reaction.
So,
0.3794 mol of oxygen gas are produced when
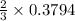 moles of potassium chlorate undergoes reaction.
moles of potassium chlorate undergoes reaction.
Moles of potassium chlorate reacted = 0.2529 moles
(b)
We are given:
Vapor pressure of water = 17.5 mmHg
Total vapor pressure = 753 mmHg
Vapor pressure of Oxygen gas = Total vapor pressure - Vapor pressure of water = (753 - 17.5) mmHg = 735.5 mmHg
To calculate the amount of Oxygen gas collected, we use the equation given by ideal gas which follows:
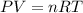
where,
P = pressure of the gas = 735.5 mmHg
V = Volume of the gas = 9.99 L
T = Temperature of the gas =
![20^oC=[20+273]K=293K](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/2rqkt68ddzsgrhhdiygdxv8hg4exf1j7bf.png)
R = Gas constant =
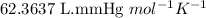
n = number of moles of oxygen gas = ?
Putting values in above equation, we get:
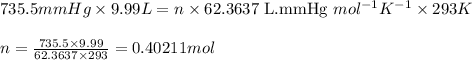
Moles of Oxygen gas = 0.40211 moles
Molar mass of Oxygen gas = 32 g/mol
Putting values in above equation, we get:

Hence, the amount of oxygen gas collected will be 12.8675 g