Answer:
Potential Energy at the top = 3.528 J
Kinetic Energy when reaching the ground = 3.528 J
Speed when hitting the ground: 5.94
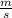
Step-by-step explanation:
a) recall the formula for the potential gravitational energy: m*g*h
(mass times the acceleration of gravity times the height at which the object is located relative to ground)
In this case the mass is 0.2 kg, the Height is 1.8 m and gravity is 9.8 m/s^2. All these in Si units, so their product will also give SI units: Joules.
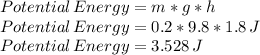
b) As the pear reaches the ground, its Potential Energy has been converted in Kinetic Energy, therefore the pear's Kinetic Energy at reaching the ground is also: 3.528 J
c) To find the pear's speed we use the Kinetic Energy formula:
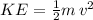
where v represents the pear's speed. We replace the appropriate values for our case: KE = 3.528 J, mass = 0.2 kg, and solve for the speed:
