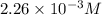Answer: The equilibrium concentration of HCl is
Step-by-step explanation:
We are given:
Moles of
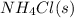 = 0.564 moles
= 0.564 moles
Volume of vessel = 1.00 L
Molarity is calculated by using the equation:
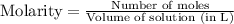
Molarity of
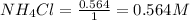
The given chemical equation follows:
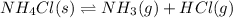
Initial: 0.564
At eqllm: 0.564-x x x
The expression of
 for above equation follows:
for above equation follows:
![K_c=[NH_3][HCl]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/yxzvlbvmujmy3wmz2zddurgfw2ssyi566j.png)
The concentration of pure solid and pure liquid is taken as 1.
We are given:
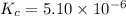
Putting values in above equation, we get:
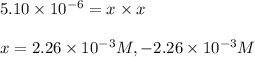
Negative sign is neglected because concentration cannot be negative.
So,
![[HCl]=2.26* 10^(-3)M](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/pdbkp44fy7ld60aozs5fwwovy0kbyaaqqc.png)
Hence, the equilibrium concentration of HCl is