Answer: Yes, the solute is a weak electrolyte
Step-by-step explanation:
Depression in freezing point is given by:
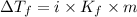
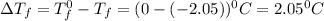 = Depression in freezing point
= Depression in freezing point
i= vant hoff factor = ?
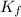 = freezing point constant =
= freezing point constant =
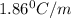
m= molality
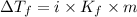
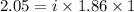
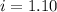
As i for non electrolytes is 1, the given compound must be an electrolyte and a weak electrolyte as the value is only slightly greater than 1.