Answer: -7956 J
Explanation:
Equilibrium constant is defined as the ratio of concentration of products to the concentration of reactants each raised to the power their stoichiometric ratios. It is expressed as
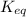
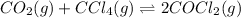
The expression for
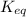 is written as:
is written as:
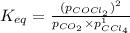
![K_(eq)=([0.745]^2)/(0.140* 0.160)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/5hrfcb9eh98nq266tb6bridlpjcd7cge30.png)
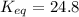
The Gibbs free energy is related to equilibrium constant by following relation:
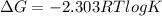
R = gas constant = 8.314 J/Kmol
T = temperature in kelvin =
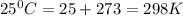
K = equilibrium constant
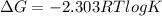
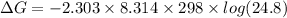
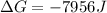
Thus ΔG for this reaction at 25 ∘C is -7956 J