Answer:
P = 359.8 atm
Step-by-step explanation:
The van der Waals' equation relates the properties of a gas, introducing constants "a" and "b" in order to consider gases as real gases. The equation is:
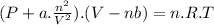
where,
P: pressure
a: correction factor for intermolecular forces
V: volume
b: correction factor for molecules' volume
n: moles
R: ideal gas constant
T: absolute temperature
