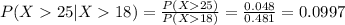Answer:
a)
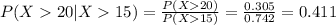
b)
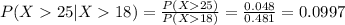
Explanation:
Previous concepts
Normal distribution, is a "probability distribution that is symmetric about the mean, showing that data near the mean are more frequent in occurrence than data far from the mean".
The Z-score is "a numerical measurement used in statistics of a value's relationship to the mean (average) of a group of values, measured in terms of standard deviations from the mean".
Let X the random variable that represent the interpupillary distance (the distance between the pupils of the left and right eyes) of a population, and for this case we know the distribution for X is given by:
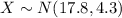
Where
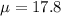 and
and
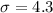
And let
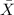 represent the sample mean, the distribution for the sample mean is given by:
represent the sample mean, the distribution for the sample mean is given by:
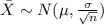
On this case
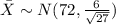
Part a
(a) What is the probability that the waiting time will exceed 20 minutes, given that it has exceeded 15 minutes?
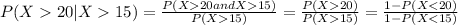
We can find the inidivual probabilities like this:
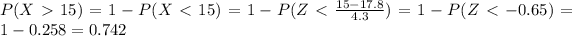
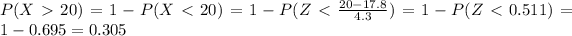
And then we can replace
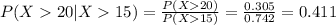
Part b
(b) What is the probability that the waiting time will exceed 25 minutes, given that it has exceeded 18 minutes?
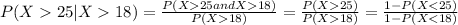
We can find the inidivual probabilities like this:
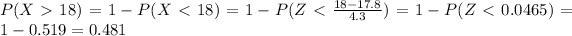
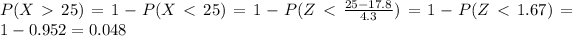
And then we can replace