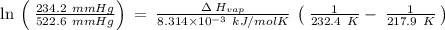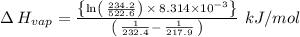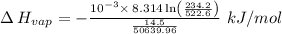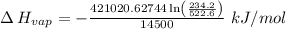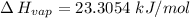Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
The expression for Clausius-Clapeyron Equation is shown below as:
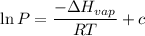
Where,
P is the vapor pressure
ΔHvap is the Enthalpy of Vaporization
R is the gas constant (8.314×10⁻³ kJ /mol K)
c is the constant.
For two situations and phases, the equation becomes:
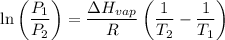
Given:
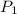 = 234.2 mmHg
= 234.2 mmHg
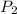 = 522.6 mmHg
= 522.6 mmHg
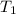 = 217.9 K
= 217.9 K
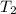 = 232.4 K
= 232.4 K
So,