Answer:
Temperature = 44.02°C
Step-by-step explanation:
Insulated container indicates no heat loss to the surroundings.
The specific heat capacity of a substance is a physical property of matter. It is defined as the amount of heat that is to be supplied to a unit mass of the material to produce a unit change in its temperature.
The SI unit of specific heat is joule per kelvin and kilogram, J/(K kg).
Now,
specific heat for water is 4.1813 Jg⁻¹K⁻¹.
Latent heat of vaporization of water is 2257 Jg⁻¹.
Energy lost by steam in it's process of conversion to water, is the energy acquired by water resulting in an increase in it's temperature.
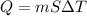
Q= Heat transferred
m= mass of the substance
T= temperature
Also,
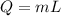
L= Latent heat of fusion/ vaporization ( during phase change)
Now applying the above equations to the problem:
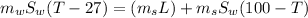
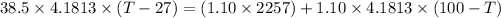
Temperature = 44.02°C