Answer:
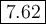
Step-by-step explanation:
1. pH of original buffer
(a) Calculate pKₐ
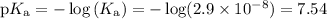
(b) Calculate the pH
We can use the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation to get the pH.
![\begin{array}{rcl}\text{pH} & = & \text{pK}_{\text{a}} + \log \left(\frac{[\text{A}^(-)]}{\text{[HA]}}\right )\\\\& = & 7.54 +\log \left((0.450)/(0.450)\right )\\\\& = & 7.54 + \log1.00 \\ & = & 7.54 + 0.00\\& = & 7.54\\\end{array}](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/ohjkglthoohp3uy67ip143imnf17k3nhsm.png)
2. pH after adding strong base
(a) Find new composition of the buffer
The base reacts with the HA and forms A⁻

HA + OH⁻ ⟶ A⁻ + H₂O
I/mmol: 450 40 450
C/mmol: -40 -40 40
E/mmol: 410 0 490
(b) Find the new pH
![\begin{array}{rcl}\text{pH} & = & \text{pK}_{\text{a}} + \log \left(\frac{[\text{A}^(-)]}{\text{[HA]}}\right )\\\\& = & 7.54 +\log \left((490)/(410)\right )\\\\& = & 7.54 + \log1.195 \\& = & 7.54 +0.0774\\& = & \mathbf{7.62}\\\end{array}\\\text{The new pH is $\large \boxed{\textbf{7.62}}$}](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/xyrx4eflopyiakngkcjjag3st135znf6ho.png)