Answer:
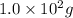
Step-by-step explanation:
Depression in freezing point is given by:
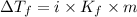
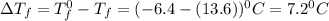 = Depression in freezing point
= Depression in freezing point
i= vant hoff factor = 1 (for non electrolyte like urea)
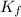 = freezing point constant =
= freezing point constant =
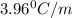
m= molality
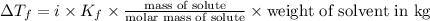
Weight of solvent (X)= 950 g = 0.95 kg
Molar mass of non electrolyte (urea) = 60.06 g/mol
Mass of non electrolyte (urea) added = ?
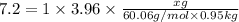
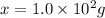
Thus
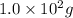 urea was dissolved.
urea was dissolved.