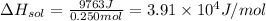Answer:
3.91 × 10⁴ J/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
We can calculate the heat of solution using the following expression.
Q = c × m × ΔT
where,
c is the specific heat capacity of the solution
m is the mass of the solution
ΔT is the change in the temperature
The mass of LiCl is:
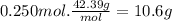
The mass of the solution is:
m = mLiCl + mH₂O = 10.6 g + 200.0 g = 210.6 g
Q = c × m × ΔT = (4.184 J g⁻¹ °C⁻¹) × 210.6 g × 11.08 °C = 9763 J
In a constant pressure calorimeter, the molar enthalpy of solution for LiCl is: