Answer:
We reject the null hypothesis.
Explanation:
We are given the following information in the question:
Sample size, n = 71
Population variance is known.
Level of significance, α = 0.08
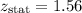
The null and alternate hypothesis are:
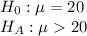
We use one-tailed z test to perform this hypothesis.
Formula:
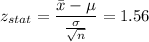
Now,
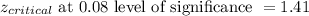
Since,
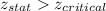
We fail to accept the null hypothesis and reject it and accept the alternate hypothesis.