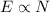Answer:
0.0027 V
0.000625 V
EMF doubles
Step-by-step explanation:
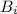 = Initial magnetic field = 0.2 T
= Initial magnetic field = 0.2 T
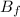 = Final magnetic field = 1.4 T
= Final magnetic field = 1.4 T
t = Time taken = 1.6 s
A = Area
N = Number of turns
Induced emf is given by
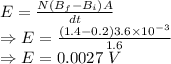
Emf is 0.0027 V
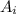 = Initial area =
= Initial area =
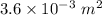
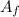 = Final area =
= Final area =
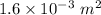
B = 0.5 T
Induced emf is given by
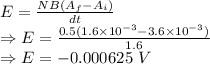
The new emf in the loop will be 0.000625 V (magnitude)
If the number of turns is doubled then the emf doubles as