Step-by-step explanation:
The given data is as follows.
Volume = 5.8 L, Pressure = 1.00 atm
T =
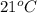 = (21 + 273) K = 294 K, mass = 6.7 g
= (21 + 273) K = 294 K, mass = 6.7 g
R = 0.0821 Latm/mol K
According to the ideal gas equation, we will calculate the number of moles as follows.
PV = nRT
or, n =
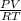
Hence, putting the given values into the above formula as follows.
n =
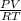
=

= 0.24 mol
Now, calculate molar mass of the gas as follows.
Molar mass =
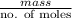
=
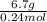
= 27.91 g/mol
or, = 28 g/mol (approx)
As the gas is diatomic so, mass of two atoms of gas X is 28 g/mol. And, mass of one atom of gas is as follows.
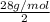
= 14 g/mol
Hence, nitrogen atom has a mass of 14 g/mol. Therefore, we can conclude that the given diatomic gas is
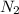 .
.