Answer: The standard reduction potential for reduction half reaction is 1.82 V
Step-by-step explanation:
The given chemical reaction follows:
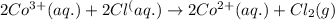
Oxidation half reaction:
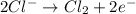
Reduction half reaction:
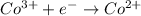
Substance getting oxidized always act as anode and the one getting reduced always act as cathode.
To calculate the
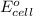 of the reaction, we use the equation:
of the reaction, we use the equation:
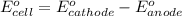
We are given:
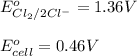
Putting values in above equation, we get:
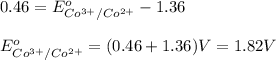
Hence, the standard reduction potential for reduction half reaction is 1.82 V