Answer:
h = 89.6 W/m^2 K
Step-by-step explanation:
Given data:
altitude is 10 km
speed of airplane is 800 km/h
coeeficent of frcition is 0.0016
From standard table
for - 50 degree C and 1 atm pressure
Cp= 999 J/kg K
P_r = 0.744 for reynold's analogy
From Gas law we have
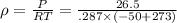
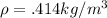
from Modified Reynolds analogy we have
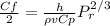
solving for h so we have
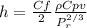
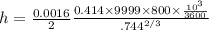
h = 89.6 W/m^2 K