Answer: 0.8238
Explanation:
Given : Scores on a certain intelligence test for children between ages 13 and 15 years are approximately normally distributed with
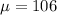 and
and
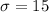 .
.
Let x denotes the scores on a certain intelligence test for children between ages 13 and 15 years.
Then, the proportion of children aged 13 to 15 years old have scores on this test above 92 will be :-
![P(x>92)=1-P(x\leq92)\\\\=1-P((x-\mu)/(\sigma)\leq(92-106)/(15))\\\\=1-P(z\leq })\\\\=1-P(z\leq-0.93)=1-(1-P(z\leq0.93))\ \ [\because\ P(Z\leq -z)=1-P(Z\leq z)]\\\\=P(z\leq0.93)=0.8238\ \ [\text{By using z-value table.}]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/high-school/6ot6natlspi70qchfu5ij2cpcmqxgx18jk.png)
Hence, the proportion of children aged 13 to 15 years old have scores on this test above 92 = 0.8238